IPv4
From $0.70 for 1 pc. 41 countries to choose from, rental period from 7 days.
IPv4
From $0.70 for 1 pc. 41 countries to choose from, rental period from 7 days.
IPv4
From $0.70 for 1 pc. 41 countries to choose from, rental period from 7 days.
IPv6
From $0.07 for 1 pc. 14 countries to choose from, rental period from 7 days.
ISP
From $1.35 for 1 pc. 23 countries to choose from, rental period from 7 days.
Mobile
From $14 for 1 pc. 14 countries to choose from, rental period from 2 days.
Resident
From $0.90 for 1 GB. 200+ countries to choose from, rental period from 30 days.
Use cases:
Use cases:
Tools:
Company:
About Us:
When people think of fake IP addresses, many associate them with something illegal such as hacking, cyberattacks, or data spoofing. In reality, it’s much simpler and completely legal. A fake IP technique is not the act of trying to access a device, but changing the address used to connect on the internet.
The aim for such actions is anonymity, privacy protection while skipping blocks and some sort of restrictions based on user geolocation. Spoofing your IP allows for hiding one's real location, accessing geographically restricted content, or aiding in saving the user from online tracking.
This article discusses: can you fake an IP address without any special skills involved, what is often relied upon to achieve this, and common tools to that end.
There are several such methods to mask or change it. Some approaches are simple to execute, while others require a certain technical skill. Each of these approaches has some sort of performance attributes, constraints, and use cases scenarios.
If you're asking, "how can i get a fake IP address?” the answers are as follows:
Next, we highlight and explain the most common methods.
Virtual Private Network services provide one of the most reliable options to change your address. In fact, with a VPN, all internet traffic is not only routed through an overseas remote server but also encrypted—and so, for any service dedicated to tracking users, the IP being logged is that of the VPN server and not the original address associated with the user.
Let’s illustrate the concept of a fake IP address example utilizing VPN.
Real IP:
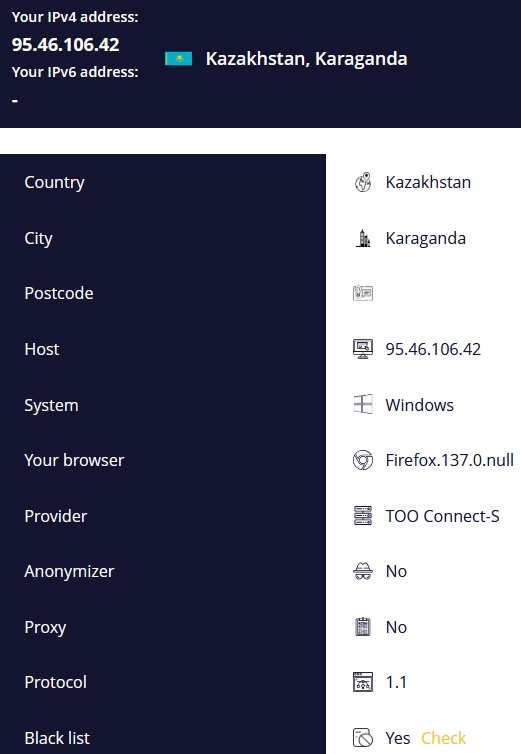
After connecting via VPN:
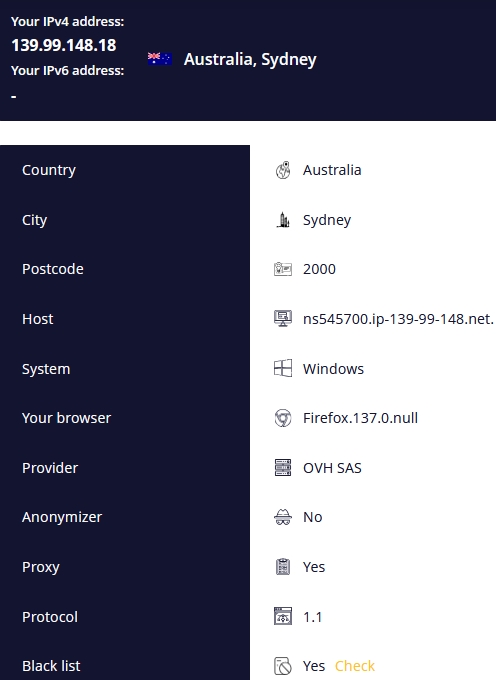
This approach is best when seeking access to geo-blocked content like streaming services, news websites, or online shops—not available in your country. VPNs also protect personal data in public hotspot networks and improve privacy level overall.
Benefits of VPNs:
Some of the drawbacks include: reduced connection speed, paid features within basic plans, and app installation requirements.
Proxy servers act as intermediaries between the user and the web page being accessed. They carry out all the functions of an interpreter. The intermediary server fetches the user’s data, interprets it, and then conveys it to the appropriate IP. In this manner, the proxy is displayed instead of the actual user address.
Unlike VPNs that encrypt all traffic and operate on the OS level, proxies work selectively—they can be set up for one browser, application, or even a specific script. Proxies are useful within a particular area. They can be perfectly suitable for scraping, testing, marketing, and managing multiple accounts.
Its types by protocols are split into:
Differences in anonymity, stability and trust levels come from the type of address provided through proxies.
These IPs are from data centers. They are fast, inexpensive, and easy to scale. They are best for high-volume tasks such as price monitoring, data harvesting, and mass-traffic creation.
Downsides: they can be detected easily and more often than not are banned from Amazon and Google.
These are linked to real users and assigned by ISPs. Websites consider this type of connection as authentic. Great for bypassing anti-bot systems, verifications, advertisement checks, and traffic arbitrage.
Downsides: relatively expensive with less stable speeds than other types.
Works through mobile carrier networks (3G, 4G, LTE). The most anonymous type – used when others fail, such as in mobile SMM or traffic arbitrage.
Downsides: the most expensive, often have limitations in speed and bandwidth.
These are a combination of residential and datacenter types. They are issued from data centers but registered with actual ISPs. Also, they are more secure and harder to block than standard datacenter ones without losing speed and dependability.
Downsides: fewer options available on the market and more costly than datacenter ones.
Intermediary servers are perfect for assisting with tasks that require speed and dynamic IP control. They are perfect for performing test runs of a web application, automating processes, scraping data, social media marketing, or account management. This is particularly the case when we have to work with dozens or even hundreds of distinct IPs.
It is also worth remembering that the higher the degree of masking, the more expensive the proxy will be. Therefore, the selection will depend on the specific goals ranging from anonymity with a browser to automation and extensive research operations.
Dozens of browser extensions allow users to change it with a click. In Chrome, for example, a fake IP address can be set utilizing such addons:
Such tools are highly useful for accessing content restricted due to geographical barriers. They serve the vital function of offering anonymity while surfing the web.
Through browser system settings, users can be guided from this link to set fake IP addresses and verify if the changes were successfully implemented using services displaying the current IP and related information.
For Windows computers, a fake IP address can be set in multiple ways. One method is changing the network settings bypassing them on purpose, like setting static IP in your connection properties as shown in this guide.
However, it’s often better to implement third-party software, VPN clients or proxy managers. These will let you change IP with ease, some even do it automatically at intervals you choose.
OpenVPN, Windscribe, and Proxifier are some of the suggested ones. Advanced antivirus and firewall software also have built-in features which you can exploit.
As for automation purposes, developers may find the need to generate fake IP addresses. Such as when sending HTTP requests from different IPs. This can be achieved in Python with various libraries:
As such a script could be made that enhances anonymity by changing the IP for each request sent. That said, this is one of the most robust methods for automation or scraping purposes.
Multiple options are available that enable utilizing a falsified address. Their functionalities, levels of security, and use cases vary. Below are the most common types of software used for masking traffic and maintaining anonymity on the Internet.
Modern VPNs encrypt traffic, obfuscate your real IP, and allow selection of servers from myriad countries. Popular options include:
VPN clients are especially effective for passing through public Wi-Fi, bypassing geoblocks, and ensuring privacy.
These programs assist with managing vast quantities of servers. They are used in automation, scraping, and testing for advanced setup in configuration.
Popular tools include:
Indeed, such special managers come in handy when you need to use multiple IPs and need to control and manage them effectively.
These are the types of browsers that are tailored to mimic distinct users on the internet. They also alter your IP, browsing fingerprints, geographical location, type of device, and many more.
Most popular antidetect solutions at this moment are :
These tools are prominent in traffic arbitrage, marketing, multi-accounting, advertisement testing, and account management.
If you are searching for ways to set a fake IP address, first identify your objectives:
Having a fake IP address isn’t about fraud or circumventing the law; it’s about managing your own information. Individuals can use a variety of methods to change their digital whereabouts, remain unidentified and anonymous, protect privacy, and evade restrictions.
Practices such as these are commonly achieved with VPNs, intermediary servers, plugins, the TOR network and even Python scripts. These methods are device agnostic – Windows, macOS, phones, and even web and mobile browsers.
The user’s privacy objectives determine the tools to be deployed. For private, day to day activities, a VPN is recommended. For more technical, automation, or backend work, proxies and scripts will be useful. For sophisticated operations, antidetect solutions are recommended.
As a reminder, your security and reliability are always at stake, because of the services you integrate. Always choose VPN and proxy service providers that guarantee trusted encryption, stability, unbreachable privacy policies, and flawless operational records.
