IPv4
From $0.70 for 1 pc. 40 countries to choose from, rental period from 7 days.
IPv4
From $0.70 for 1 pc. 40 countries to choose from, rental period from 7 days.
IPv4
From $0.70 for 1 pc. 40 countries to choose from, rental period from 7 days.
IPv6
From $0.07 for 1 pc. 14 countries to choose from, rental period from 7 days.
ISP
From $1.35 for 1 pc. 21 countries to choose from, rental period from 7 days.
Mobile
From $14 for 1 pc. 14 countries to choose from, rental period from 2 days.
Resident
From $0.90 for 1 GB. 200+ countries to choose from, rental period from 30 days.
Use cases:
Use cases:
Tools:
Company:
About Us:
DNS, or the Domain Name System, is essential for translating memorable domain names into IP addresses, which are used to load web pages. This translation makes it easier for users to navigate the Internet without having to remember the numeric IP addresses of websites.
DNS enhances user experience by simplifying access to web resources, allowing users to interact with the internet through familiar domain names instead of complex network addresses.
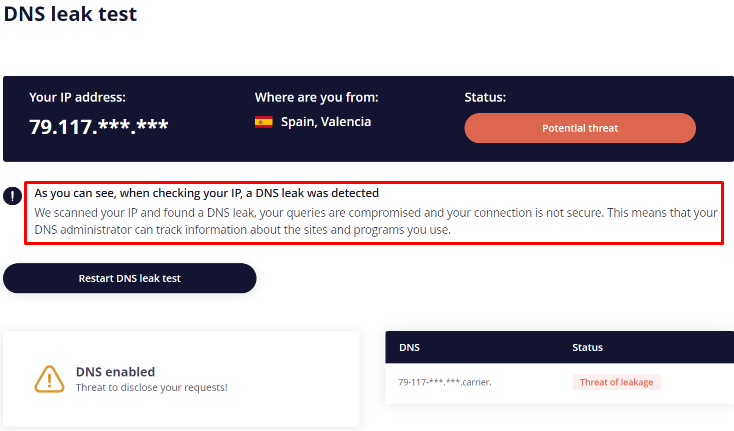
However, DNS leaks can compromise user privacy. These leaks occur when DNS requests are sent outside of a secure connection, potentially allowing Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and third parties to track a user's online activities. This risk is heightened when using services meant to anonymize user activity, as DNS leaks can expose real user information, including browser history. To maintain anonymity online, it is crucial to implement safeguards against DNS leaks.
Indirect signs of a DNS leak can include slow internet speeds, unexpected pop-up ads, and accessing websites that should be blocked by a VPN. Let’s delve deeper into the main causes of DNS leaks:
To mitigate these issues, it’s crucial to use tools specifically designed to detect DNS leaks and ensure that your connection remains secure.
There are several types of tools that can be used to check for DNS leaks. These include traffic monitoring programs, WebRTC leak tests, and other technologies that can reveal real user data, as well as online checkers. Let's explore these methods in more detail:
Checking for DNS leaks using online checkers is the fastest and easiest method. You can perform this check using our website:
It is also recommended to use the WebRTC check since the activity of this technology can contribute to DNS leaks. This tool operates on the same principle as the DNS checker and immediately displays the result. If a leak is detected, it is advised to disable the use of WebRTC. You can find step-by-step instructions on how to do this in this article.
There are several effective methods to protect against DNS leaks, including the use of private proxy servers, setting up reliable DNS servers, and activating the DNS over HTTPS option. Below, we will explore how to implement each of these methods.
Using anonymization tools such as a proxy allows for the encryption of traffic, including DNS, and routes it through a secure tunnel. There are various ways to configure a proxy server:
The most versatile method involves using the “Proxifier” program. By clicking on this link, you can access detailed instructions on how to set it up.
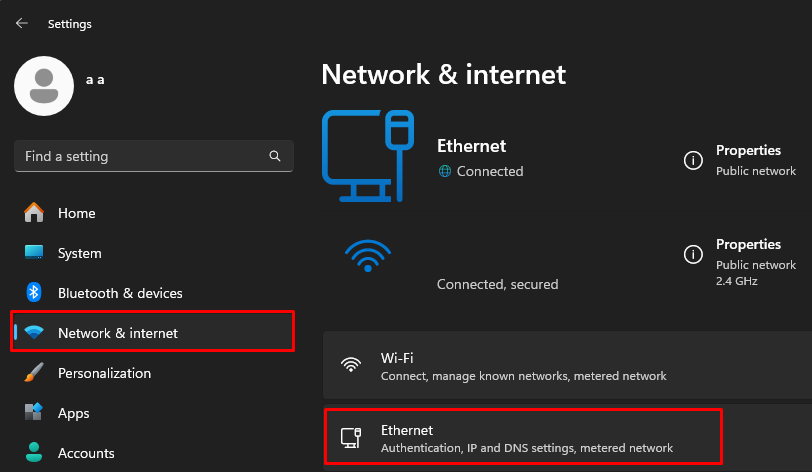
Manually setting up a specific public DNS server in your system can enhance privacy by avoiding the use of ISP servers for DNS requests. Here’s how to set this up using Windows 11:
![]()
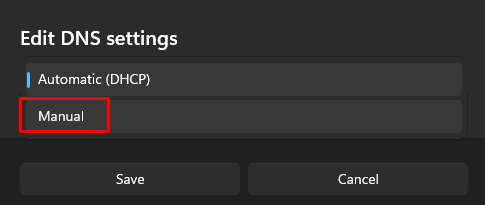
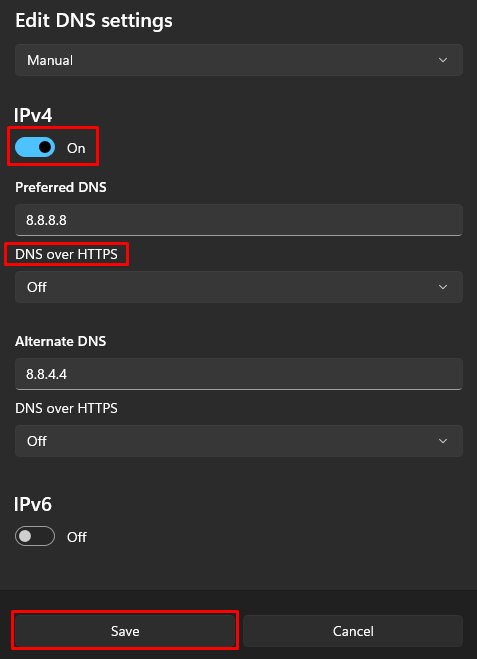
This process completes the DNS setup. If you wish to revert to using your ISP’s DNS settings, simply switch the DNS settings back to automatic.
You can simplify the process of manually setting up DNS by utilizing DNS over HTTPS (DoH) technology in any popular browser. This protocol encrypts DNS requests via HTTPS, enhancing both security and privacy. Here’s how to activate it in the Opera GX browser:
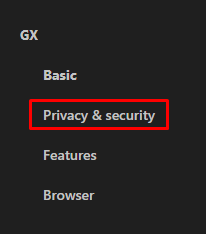
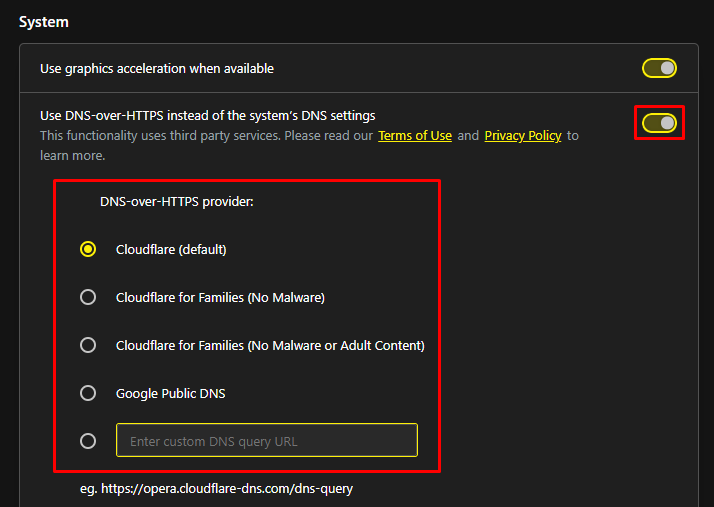
For best results, ensure you select only reliable DNS servers from reputable providers.
There is a wide variety of DNS services available on the market today, each offering its own set of features and benefits. Popular options include Google Public DNS, Cloudflare, OpenDNS, and 1.1.1.1. Besides providing the basic functionality of DNS resolution, many of these services also offer additional security features.

The service offers its own DNS servers along with access to the DNS-over-HTTPS (DoH) option. This enhances privacy by making it more difficult for providers to access user requests and prevents the collection of user data statistics. Below are the DNS servers of various formats:
IPv4:
IPv6:

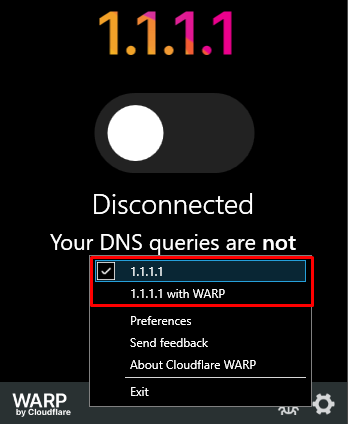
The 1.1.1.1 app from Cloudflare is designed to enhance both the speed and security of your internet connection by utilizing the 1.1.1.1 DNS server. It incorporates technologies such as DNS over HTTPS (DoH) and DNS over TLS (DoT) to encrypt DNS requests, significantly increasing privacy and protecting users from monitoring and censorship.
The application is compatible with iOS, Android, MacOS, Windows, and Linux platforms. Importantly, 1.1.1.1 is available free of charge. It operates in two modes: 1.1.1.1 and 1.1.1.1 with Warp, with key differences in protection level and connection speed:
To activate the app, simply choose an operating mode and toggle the slider in the main menu.

This service provides public DNS addresses from Google that users can manually configure on their devices. There are two types of addresses available:
IPv4:
IPv6:
These IPv6 addresses are for networks operating on IPv6, the latest Internet protocol. IPv6 offers significantly more addresses and enhanced security features compared to previous protocols.

It operates similarly to Google Public DNS but includes additional features such as the ability to verify DNS activation post-setup via the official website. If you register on the site, you gain access to enhanced functionalities:
OpenDNS also provides various tools for deeper control and analysis of Internet traffic.
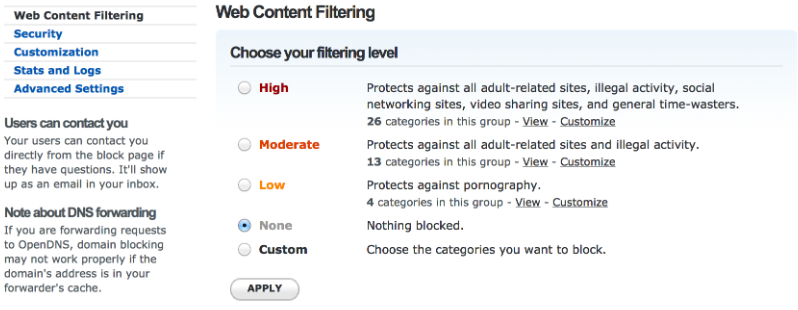
OpenDNS Servers:
Given the crucial role of DNS in Internet communications, it is advisable to carefully select and configure DNS servers. Google Public DNS and Cloudflare require manual configuration, whereas the 1.1.1.1 app provides a user-friendly interface with selectable connection modes. OpenDNS is ideal for users needing advanced tools to monitor and control Internet traffic. Utilizing these services helps prevent DNS leaks and enhances security, complementing other anonymization methods such as proxies.
